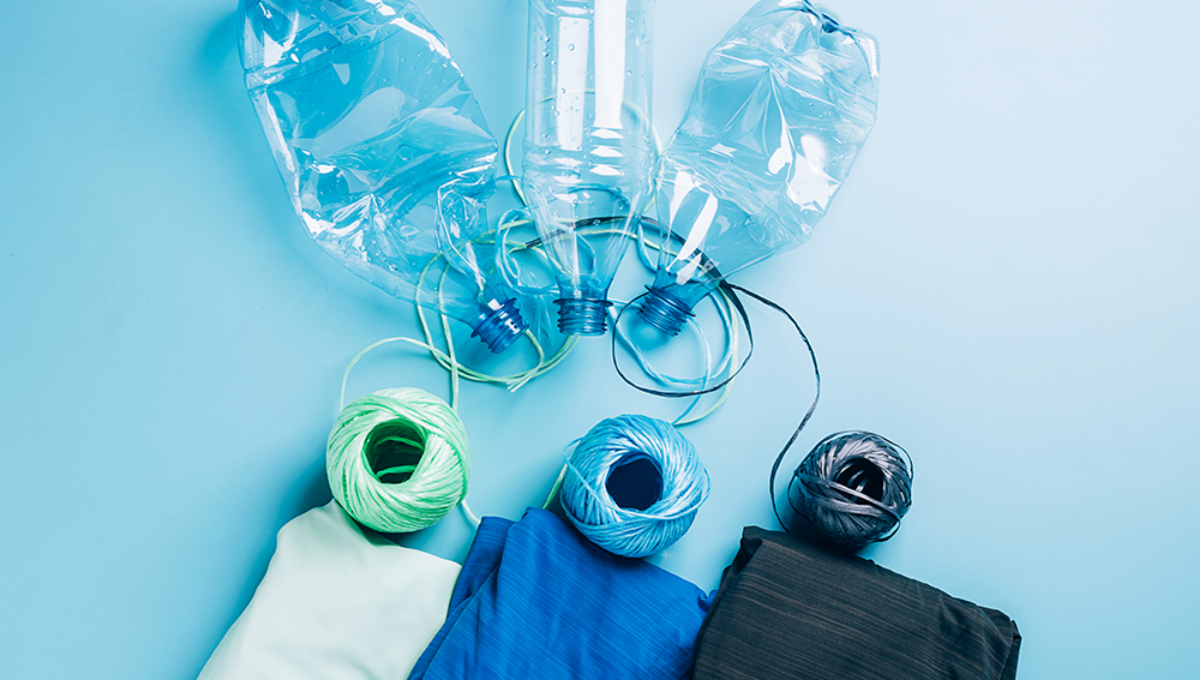
Introduction
Green textiles are changing the way the world thinks about fabrics. In the past, the textile industry was often linked with waste, heavy energy use, and pollution. Today, however, more companies and consumers are pushing for sustainable options. One of the most promising solutions is thermomechanical recycled polyester. This process transforms plastic waste into usable fibers without relying on complex chemicals. It offers strength, durability, and lower environmental impact. As a result, thermomechanical recycled polyester has become central to the rise of green textiles around the world.
Understanding Green Textiles
Green textiles are fabrics that aim to reduce harm to the environment. They may come from natural fibers, recycled materials, or innovative technologies that cut down on water, energy, and chemicals. Unlike traditional fabrics, green textiles focus on a circular approach. Instead of a “make, use, and throw away” model, these textiles encourage reuse, recycling, and regeneration.
Thermomechanical recycled polyester is one of the best examples. By reusing plastic bottles, packaging waste, and old textiles, this method gives a second life to materials that would otherwise pollute oceans or landfills. The outcome is a fabric that supports sustainability while still delivering the durability expected from polyester.
What Is Thermomechanical Recycled Polyester?
Thermomechanical recycling is a process where polyester waste is cleaned, shredded, and melted. The molten material is then spun into new fibers. Unlike chemical recycling, this method does not break down materials into their base molecules. Instead, it reshapes the polyester mechanically.
This process uses less energy, avoids strong chemicals, and creates fibers suitable for clothing, upholstery, and industrial applications. Importantly, it proves that green textiles do not need to sacrifice performance to achieve sustainability.
Why Thermomechanical Recycling Matters for Green Textiles
The importance of thermomechanical recycled polyester can be seen in its many benefits:
-
Waste Reduction: Billions of plastic bottles are thrown away each year. Recycling them into textiles reduces waste.
-
Lower Energy Use: Compared to virgin polyester, the process uses significantly less energy.
-
Reduced Emissions: Less energy means fewer carbon emissions, making it better for the climate.
-
Resource Conservation: Recycled polyester reduces the demand for crude oil, which is the base material for virgin polyester.
Because of these reasons, thermomechanical recycled polyester plays a vital role in building a future where green textiles dominate global markets.
Environmental Impact of Green Textiles
Textiles are responsible for a large share of environmental damage. Traditional polyester production requires heavy use of fossil fuels and emits harmful greenhouse gases. By contrast, thermomechanical recycled polyester reduces emissions and reuses materials already in circulation.
For example, producing recycled polyester can save up to 60% of the energy compared to virgin polyester. It also lowers water use and reduces the release of harmful chemicals. These benefits highlight how green textiles offer real solutions for environmental problems.
Advantages of Thermomechanical Recycled Polyester
Thermomechanical recycled polyester offers many strengths that make it ideal for green textiles:
-
Durability: The fibers are strong and long-lasting, much like virgin polyester.
-
Flexibility: They can be used in clothing, bags, furniture, and packaging.
-
Consumer Appeal: Shoppers are more likely to buy products labeled as eco-friendly.
-
Affordability: Mechanical recycling often costs less than chemical recycling.
Together, these benefits make recycled polyester a preferred option for companies moving toward sustainable production.
Limitations and Challenges
While thermomechanical recycled polyester is valuable, it does face some issues:
-
Fiber Quality: With each recycling cycle, the fibers lose a bit of strength and softness.
-
Color Problems: Removing dyes from waste textiles is difficult.
-
Need for Blends: To maintain quality, many fabrics combine recycled and virgin polyester.
-
Infrastructure Gaps: Recycling plants are not available in all regions.
Despite these challenges, research and new technology continue to improve the recycling process. Over time, these issues will become less limiting.
Applications of Thermomechanical Recycled Polyester in Green Textiles
Recycled polyester is now found in a wide range of products. Some of the most common uses include:
-
Fashion and Apparel: From sportswear to jackets, recycled polyester is used to meet consumer demand for sustainable fashion.
-
Home Textiles: Items like curtains, carpets, and bedding now include green textiles made with recycled polyester.
-
Industrial Products: Automotive interiors, seat covers, and construction fabrics also benefit from this material.
-
Packaging: Bottles and containers are remade from recycled polyester, closing the loop in production.
These applications show that thermomechanical recycling has moved beyond niche use and is becoming central to global textile production.
Green Textiles and Consumer Awareness
One reason green textiles are gaining momentum is growing consumer awareness. More buyers now ask about the origin of fabrics, the energy used in production, and the impact on the planet. By choosing thermomechanical recycled polyester, consumers support eco-friendly practices.
This demand pressures companies to adopt green textiles. Brands that ignore sustainability often face criticism, while those that adopt recycled materials earn loyalty and trust. Thus, consumer awareness directly fuels the expansion of green textiles.
Brands Supporting Green Textiles
Several major brands have embraced thermomechanical recycled polyester:
-
Adidas: The company has pledged to use only recycled polyester in its products by 2024.
-
Patagonia: Known for its commitment to sustainability, Patagonia has been using recycled polyester for years.
-
H&M: Their Conscious collection highlights the use of green textiles, including rPET.
-
Nike: The brand uses recycled polyester in performance wear to reduce its carbon footprint.
These examples show that both sportswear and fast-fashion companies see recycled polyester as key to their green textile strategies.
Future of Thermomechanical Recycled Polyester
The future of green textiles looks promising. Advances in recycling technology will improve fiber quality, reduce waste, and expand applications. Governments are also introducing policies to support recycling, which will push more industries to adopt thermomechanical recycled polyester.
As consumers demand sustainable products, companies that embrace green textiles will stand out. The combination of environmental need, market demand, and technological progress ensures that thermomechanical recycled polyester will remain a vital part of the textile industry.
Conclusion
Green textiles represent a new path for the fashion and textile industries. Thermomechanical recycled polyester offers a way to recycle waste, cut energy use, and reduce pollution without sacrificing performance. Although challenges remain, innovation and consumer support will drive growth.
By choosing products made from recycled polyester, people support a circular economy where waste becomes a resource. In this way, thermomechanical recycled polyester is more than a fabric—it is a symbol of sustainable progress. The rise of green textiles ensures a cleaner, healthier, and more responsible future for everyone.